Service
ANALYSIS
Staff
Mª del Pilar Burgos Domenech (Technical Manager)
Asunción Castro Pérez (Technical specialist)
Cristina Ramírez Vázquez (Technical specialist)
Mª del Rocío Campos Escobar (Technical specialist)
Rosa López Garrido (Technical specialist)
Pilar Alcántara Romano (Technical specialist)
Contact
email: analisis@irnas.csic.es
Analysis Service
Instituto de Recursos Naturales y Agrobiología de Sevilla Avda. Reina Mercedes, 10 41012 – Sevilla
Phone: 954624711
Prices
Service Requests
“Once the PDF has been downloaded and the application has been completed, it will be sent to the e-mail address indicated in the document itself, together with the complementary documentation required”.
Description of the service
IRNAS Analysis Service (SA) is part of the CSIC Scientific-Technical Services Network and its main objective is to provide instrumental and technical support to IRNAS research groups, other CSIC centers, universities, as well as other research centers, private companies and individuals who request it. In addition to this analytical support, the SA offers technical assistance to farmers and agricultural cooperatives in order to improve soil fertility. Además de este soporte analítico, el SA ofrece asistencia técnica a agricultores y cooperativas agrícolas en relación con la mejora de la fertilidad de los suelos.
Its main activities are the analysis of agricultural and environmental samples (water, soils, sediments, plants, oils, amendments, composts, agricultural residues and fertilizers) and the report and interpretation of analytical results. SA uses a variety of instrumental techniques, including inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS), inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES), segmented flow auto-analyzer, and C and N analyzer (TOC, TN), as well as classical analysis methods (volumetry and gravimetry). The service conditions, cost and delivery time depend on the type and number of samples. The conditions of the service, cost and delivery time depend on the type and number of analyses to be carried out.
Regarding quality control, the SA has internal inspection service through reference materials and external quality control through the participation in sample exchange programs (Wageningen Evaluating Programs for Analytical Laboratories, WEPAL), organized by the Department of Soil Sciences and Plant Nutrition of Wageningen University. These programs are: International Plant-analytical Exchange (IPE), International Soil-analytical Exchange (ISE) and International Manure and Refuse Sample Exchange Program (MARSEP).
On the other hand, within the training activities, the SA maintains an active teaching work through the training of students and guided visits from schools to our facilities.
Quality Commitment
Services
Soil analysis
It is a basic tool that allows soil quality knowledge from an agricultural and environmental point of view in order to improve crop fertility or solve specific problems (salinity, acidity, pollution, etc.).
The main soil testing includes: basic analysis (pH, electrical conductivity, organic matter, nitrogen, Olsen-phosphorus, available potassium, carbonates and texture), available nutrients and available micronutrients, cation exchange capacity, salinity in saturate paste extract, nitrate and ammonium contents, aqua regia extractable metals and trace elements.
Water analysis
It is important to know water quality for irrigation in order to prevent salinity or toxicity problems, as well as deciding the most suitable irrigation systems and doses. The SA main water determinations are: pH, electrical conductivity, chloride, nitrate, ammonium, alkalinity, solids, sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium, sulfate, microelements and trace elements.
Analysis and characterization of composts, amendments and fertilizers
The study of these samples is a prerequisite for their use, especially when considering the use of waste from various sources (compost, sludge, etc.). SA mainly determines: pH, electrical conductivity, organic matter, nitrogen, nutrients, microelements and trace elements.
Analysis of leaves and other plant organs
Plant analysis is an effective method to estimate nutritional status and crop nutrient requirements. The information provided by foliar analysis is a good complement to soil analysis for an agricultural farm or an experimental trial. In this case, SA offers the determination of Kjeldahl-N, macro and micronutrients, and trace elements. In addition, SA department carries out metals determination in all types of agricultural and environmental samples.
In addition to the above, the Analysis Service offers the determination of metals in all types of agricultural and environmental samples.
Equipment
Microwave digestion systems
The SA has two oven for the dissolution of solid samples through microwave-assisted digestion.
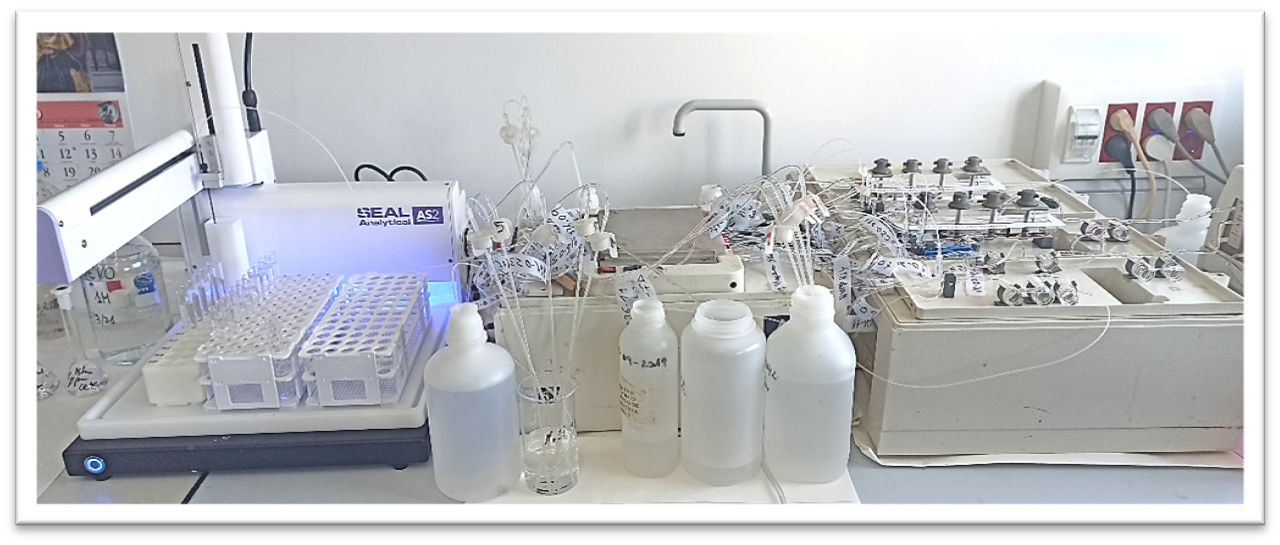
BRAN-LUEBBE multiparameter autoanalyzer
The automatic segmented flow analyzer allows the analysis of a large number of parameters (nitrogen, nitrate, nitrite, ammonium, chloride, phosphate, P-Olsen, sulfate, cyanide, etc.) in multiple types of samples (water, soil, plants, fertilizers, amendments, etc.). All of them are of great interest from an agricultural and environmental point of view, and the autoanalyzer displays results with great accuracy and low detection limits, in a short time and with low reagents consumption.
Total organic carbon analyzer and nitrogen module. SHIMADZU TOC-V SCH SHIMADZU TOC-V SCH
It allows the determination of total carbon, inorganic carbon, organic carbon (TOC) and total nitrogen present in liquid samples. Total carbon is measured by high temperature catalytic oxidation followed by non-dispersive infrared detection of CO2. For the case of inorganic carbon, the samples are HCl acidified and sparged with a carrier gas (purified air) in order to convert the inorganic carbon to CO2. Organic C is determined by the difference between total and inorganic C. Nitrogen is thermally decomposed in a combustion tube and it is detected by chemiluminescence.
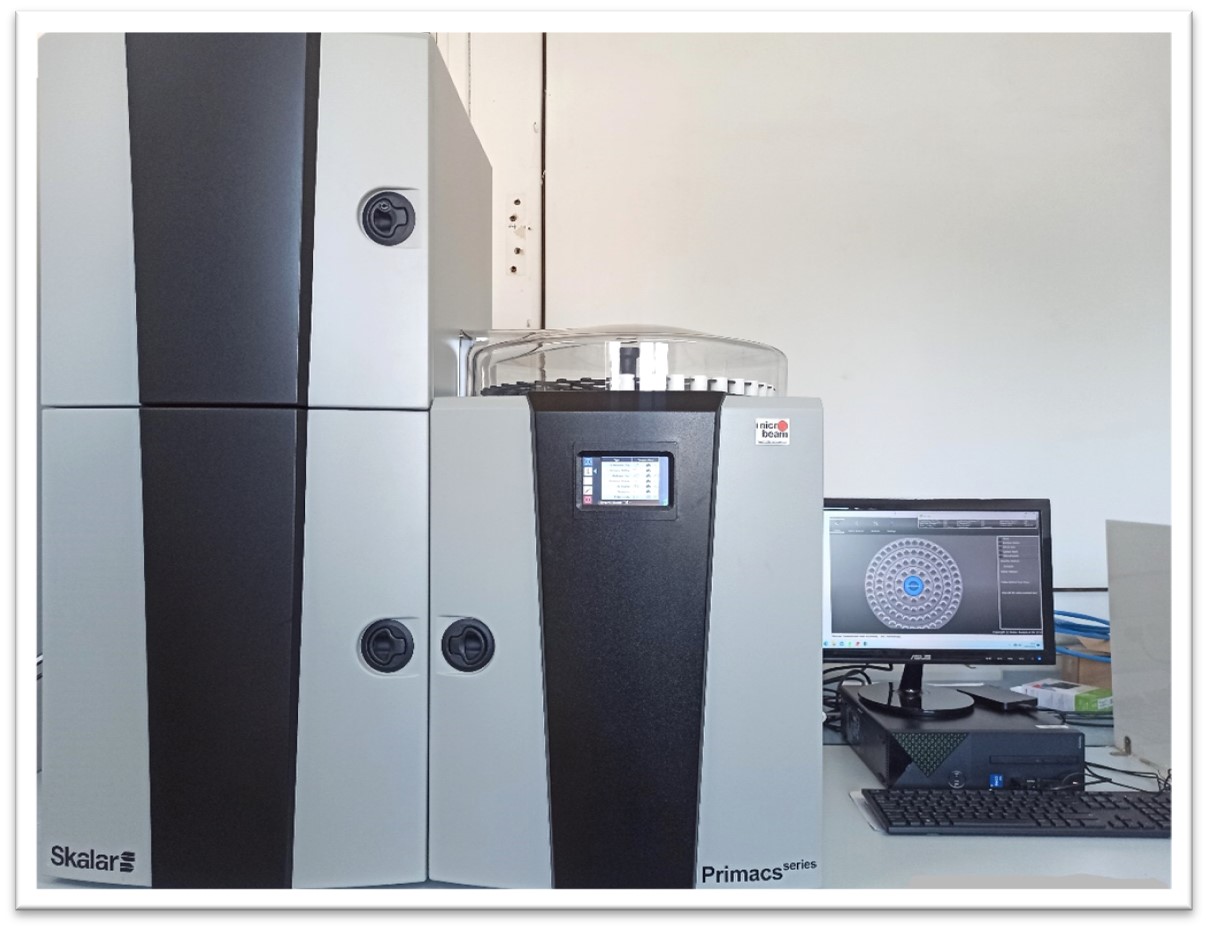
Elemental Analyzer for Carbon and Nitrogen PrimacsSNC100
This equipment is used to determine the total carbon and nitrogen content in solid or semi-liquid samples by burning the sample in pure oxygen at 1200 ᵒC. It has an autosampler and is capable of determining nitrogen (TN), total carbon (TC), total inorganic carbon (TIC) and total organic carbon (TOC).
Kjeldahl VAPOREST 50S GERHARDT Automatic Still-Titrator
This instrument allows the determination of organic nitrogen by Kjeldahl method. It is done quickly, as the distillation and titration are carried out in a single operation which is automatic and safe for the operator. It is used by boiling the sample with concentrated sulfuric acid and a catalyst, so that the oxidative destruction of the organic matter present in the sample and the decomposition of organic nitrogen to ammonia takes place. Subsequently, the ammonium is steam distillate and determined by titration.
ICP-OES VARIAN 720-ES spectrophotometer with electronic nebulizer and hydride generator
Inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy (ICP-OES) is a multielemental analysis technique capable of determining and quantifying most of the elements of the periodic table (with the exception of C, N, O, H, halogens and noble gases), in a wide range of concentrations and simultaneously. It allows the analysis of a wide range of both liquid and solid samples.
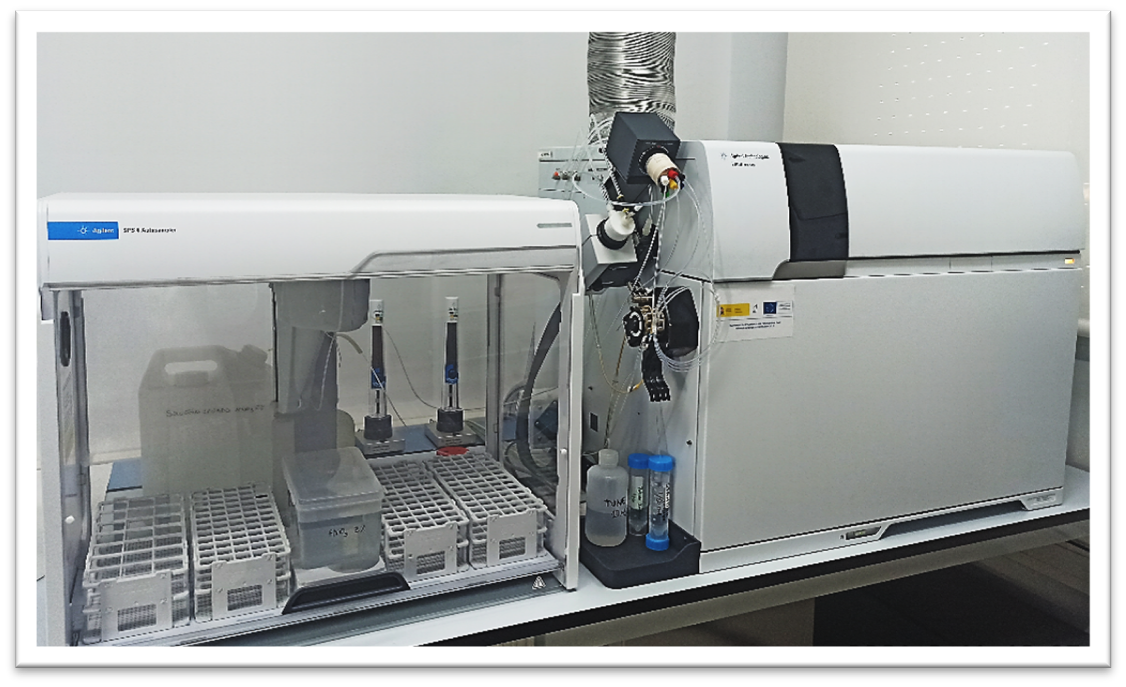
ICP-MS Agilent 7800
Inductively coupled plasma source mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) is a multielemental and isotopic inorganic analysis technique capable of determining and quantifying most of the elements of the periodic table at very low concentration levels. It can also carry out isotopic composition quantification and trace isotope stability studies.
X-RAY FLUORESCENCE ANALYZER (XRF)
The X-ray fluorescence spectrometry analyzer (XRF) is a powerful and portable unit for complete inspection in the environment in order to identify metals in soil samples, sediments, filters, etc. (around 10 mg/kg concentrations). The XRF analyzer is an advanced technology for monitoring extensive sites, for rapid analysis of containers or soils bags, sediments, metal cores, dusty cloths, surfaces and filters. The mapping of zones is facilitated, allowing a previous selection of the more representative samples in places of wide extension or variability, or the determination in samples that, due to their value, do not can be altered or taken to the laboratory, since it is a not destructive technique.